Explaining the Differences Between Universal Analytics and GA4 Data
Google Analytics 4 Vs Universal Analytics |
In UA properties, data is organized into sessions, which serve as the foundation for all reporting. A session represents a sequence of user interactions with your website within a specific timeframe. Throughout a session, Analytics captures and stores various user interactions, referred to as hits, including pageviews, events, and eCommerce transactions. Depending on how users engage with your website, a single session can consist of multiple hits.
On the other hand, in GA4 properties, session data is still available, but Analytics collects and retains user interactions with your website or app as events. Events offer valuable insights into the activities occurring on your website or app, such as pageviews, button clicks, user actions, or system events.
Moreover, events have the capability to capture and transmit additional pieces of information that provide more context or details about the user’s action. This supplementary information might encompass the purchase value, the title of the page the user visited, or the geographic location of the user.
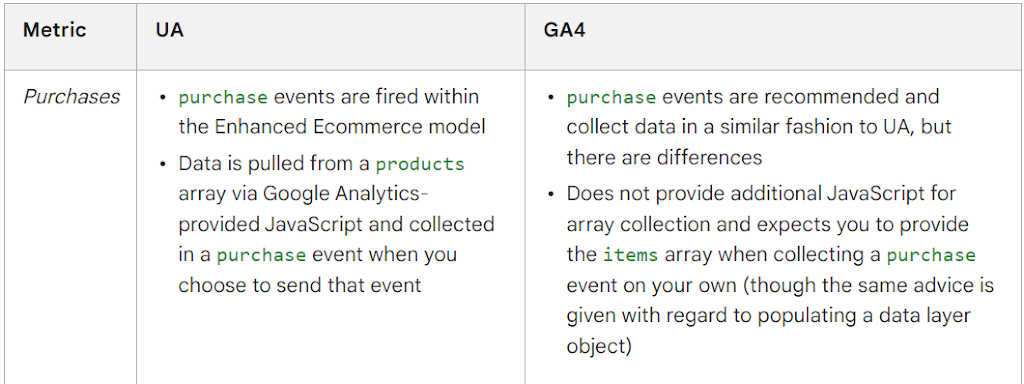
By understanding these fundamental differences between UA and GA4 data organization, you can gain insights into why your data might not align perfectly when comparing the two platforms. It is crucial to familiarize yourself with the unique features and data models of GA4 to ensure a more accurate interpretation and analysis of your analytics data.
 |
| Google Analytics 4 Vs Universal Analytics |
1. Consistent Usage of transaction_id Parameter:
The transaction_id parameter plays a significant role in data comparison. Inaccurate or inconsistent application of this parameter can result in noticeable differences between the data sets. To ensure data quality and accurate comparisons, it is essential to consistently collect transaction_id data in accordance with the documentation provided.
2. Complete Implementation of Required Parameters:
To ensure proper recording of ecommerce data in both GA4 and UA, it is important to utilize all the required parameters for ecommerce implementation. By implementing these parameters correctly, you can ensure that ecommerce data is accurately recorded and available for analysis in both platforms.